Abstract
Introduction: MicroRNA miR-1301 is embedded in intron 1 in the DNMT3A gene, which encodes the DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A, is frequently mutated in older acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (pts) & has been associated with clonal hematopoiesis. In glioma cells miR-1301 suppresses tumor cell invasion by regulating the activity & function of the p53 pathway & inhibits cell proliferation by targeting NRAS . The role of miR-1301 in AML remains to be elucidated.
Here, we investigated the clinical & prognostic impact of pri- miR-1301 in a homogenously treated set of mainly older AML pts who received allogeneic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) as consolidation.
Patients & Methods: We analyzed 126 AML pts (median age at HSCT 64 years [y]; range 38-75 y) with available pretreatment bone marrow (BM). All received HSCT after non-myeloablative (NMA) conditioning (Fludarabine 30mg/m2 at day -4 to -2 & 2Gy total body irradiation at day 0) at our institution between January 2000 & June 2012 in complete remission (CR, 83%, n=104) or CR with incomplete peripheral recovery (Cri, 17%, n=22). Cytogenetics were determined at diagnosis using standard techniques for banding & fluorescence in-situ hybridization. Using flow cytometry, BM mononuclear cells were assessed for presence of CD2, CD7, CD11b, CD13, CD14, CD15, CD33, CD34, CD38, CD45, CD56, CD61, CD64, CD65, CD117 & Glycophorin A. For pts with material available, the presence of FLT3 -ITD, FLT3 -TKD & expression status of EVI1, as well as the mutation status of the CEBPA, DNMT3A, IDH1, IDH2 & NPM1 genes were determined. Pri- miR-1301 expression was measured using a SYBR-Green assay based quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction & normalized to 18S expression as internal control. The third quartile of normalized gene expression was used to define high & low pri- miR-1301 expressers. Median follow-up after HSCT was 6.0 y for pts alive.
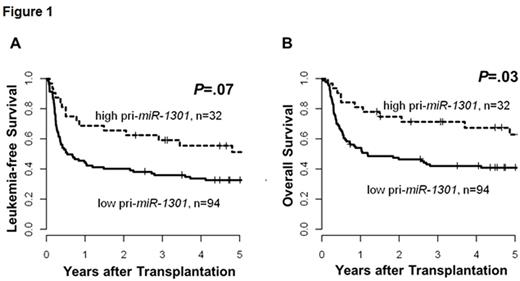
Results: At diagnosis, high pri- miR-1301 expressers had lower white blood cell counts (P=.02). High pri- miR-1301 expression associated with higher percentage of CD7 (P=.04) & by trend of CD2 (P=.10) positive cells (both T-cell associated antigens) & lower percentage of CD15 (P=.01), CD33 (P=.002) & CD64 (P=.05) positive cells (myeloid antigens). Furthermore, high pri- miR-1301 expressers were less likely to be NPM1 mutated (P=.06) by trend. Since miR-1301 is embedded in the DNMT3A gene, we tested whether pri- miR-1301 expression associated with the presence of DNMT3A mutations, but did not observe any association (pts with DNMT3A mutations: high pri- miR-1301 expression: 18% vs . low pri- miR-1301 expression: 14%, P=.73). Pts with high pri- miR-1301 expression had longer leukemia-free survival (LFS, P=.07; Figure 1A) by trend & significantly longer overall survival (OS, P=.03; Figure 1B). In multivariate analysis, high pri- miR-1301 expression retained its prognostic impact on LFS (Hazard Ratio [HR] 0.51, Confidence Interval [CI] 0.28-0.93, P=.03) after adjustment for age at HSCT, hemoglobin level at diagnosis & EVI1 expression status at diagnosis & was the only significant factor for OS (HR 0.52, CI 0.29-0.95, P=.03).
Conclusion: High pri- miR-1301 expression associated with distinct clinical & prognostic features, including higher expression of the T-cell associated antigens CD2 & CD7, lower expression of myeloid antigens CD15, CD33 & CD64 & a lower incidence of NPM1 mutations by trend. Whereas DNMT3A embedded miR-1301, no association of pri- miR-1301 expression & occurrence of DNMT3A mutation was found. Importantly, high pri- miR-1301 expressers had by trend a longer LFS & significantly longer OS independent of other prognostic markers. Further studies are warranted to elucidate the AML biology associated with high expression of the DNMT3A embedded miR-1301 in AML.
Franke: Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Pfizer: Honoraria. Schwind: Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal